Database Connection Via JNDI
To connect to DB using JNDI you have to perform the following steps:
- Log onto PaaS dashboard
- Create an environment
- Add database node into your environment
- Modify some configuration files in a web-app
- Create a connection in a java-class
Let’s do it step-by-step:
- Create environment with database (MySQL in our case):
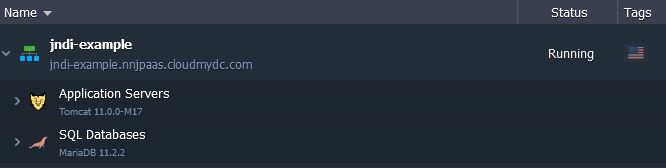
- Create a new user in a database: How to create new user - click here
Database name : jelasticDb
User_name : jelastic
Password : jelastic
- Modify configuration files in your web-application: context.xml:
<Context antiJARLocking="true" path="/JNDI">
<Resource name="jdbc/jelasticDb" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource"
maxActive="100" maxIdle="30" maxWait="10000"
username="jelastic" password="jelastic" driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://mysql-jndi-example.{hoster_domain}/jelasticDb"/>
</Context>
web.xml:
<resource-ref>
<description>MySQL Datasource example</description>
<res-ref-name>jdbc/jelasticDb</res-ref-name>
<res-type>javax.sql.DataSource</res-type>
<res-auth>Container</res-auth>
</resource-ref>
- Create connection in java-class
public class MyConnection {
private DataSource dataSource;
public MyConnection() {
try {
InitialContext context = new InitialContext();
dataSource = (DataSource) context.lookup("java:comp/env/jdbc/jelasticDb");
} catch (NamingException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(MyConnection.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
public Connection getConnection() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(MyConnection.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
return conn;
}
}